The R / Bioconductor AnVIL Package
An exploration of how workspaces provide a framework for managing data and large-scale analyses using the HCA Optimus Pipeline and 1000G-high-coverage-2019 workspaces and R using the AnVIL package.
Learning Objectives
This week we'll explore how workspaces provide a framework for managing data and large-scale analyses. We use the HCA Optimus Pipeline and 1000G-high-coverage-2019 package.
Key Resources
- Visit https://anvil.terra.bio to use the AnVIL platform.
- We use week-2-demo.R to guide us through this workshop.
- We use the HCA Optimus Pipeline and 1000G-high-coverage-2019 workspaces as examples.
- Review the Introduction to the AnVIL package vignette.
Review
Previously...
- Notes and recorded session: Using R / Bioconductor in AnVIL
Essential Steps
- Login
- Workspaces
- Billing accounts
- Cloud environment -- (R-based) Jupyter notebooks or RStudio
Cloud Computing Environment
- Runtime and persistent disk
- A 'personal' cloud computing environment
- Not shared with others
- Ephemeral
FAQs
- Persistent disk mounted at
- R / Jupyter:
/home/jupyter-user/notebooks - RStudio:
/home/rstudio
- R / Jupyter:
- Startup script or custom docker file for 'sudo'-like access, and for complete reproducibility
Workshop Activities
Setup
- Log in to AnVIL using the email address you used to register for the course and navigate (via the HAMBURGER) to Workspaces.
- If you cloned the Bioconductor-Workshop-Popup workspace last week, delete it now.
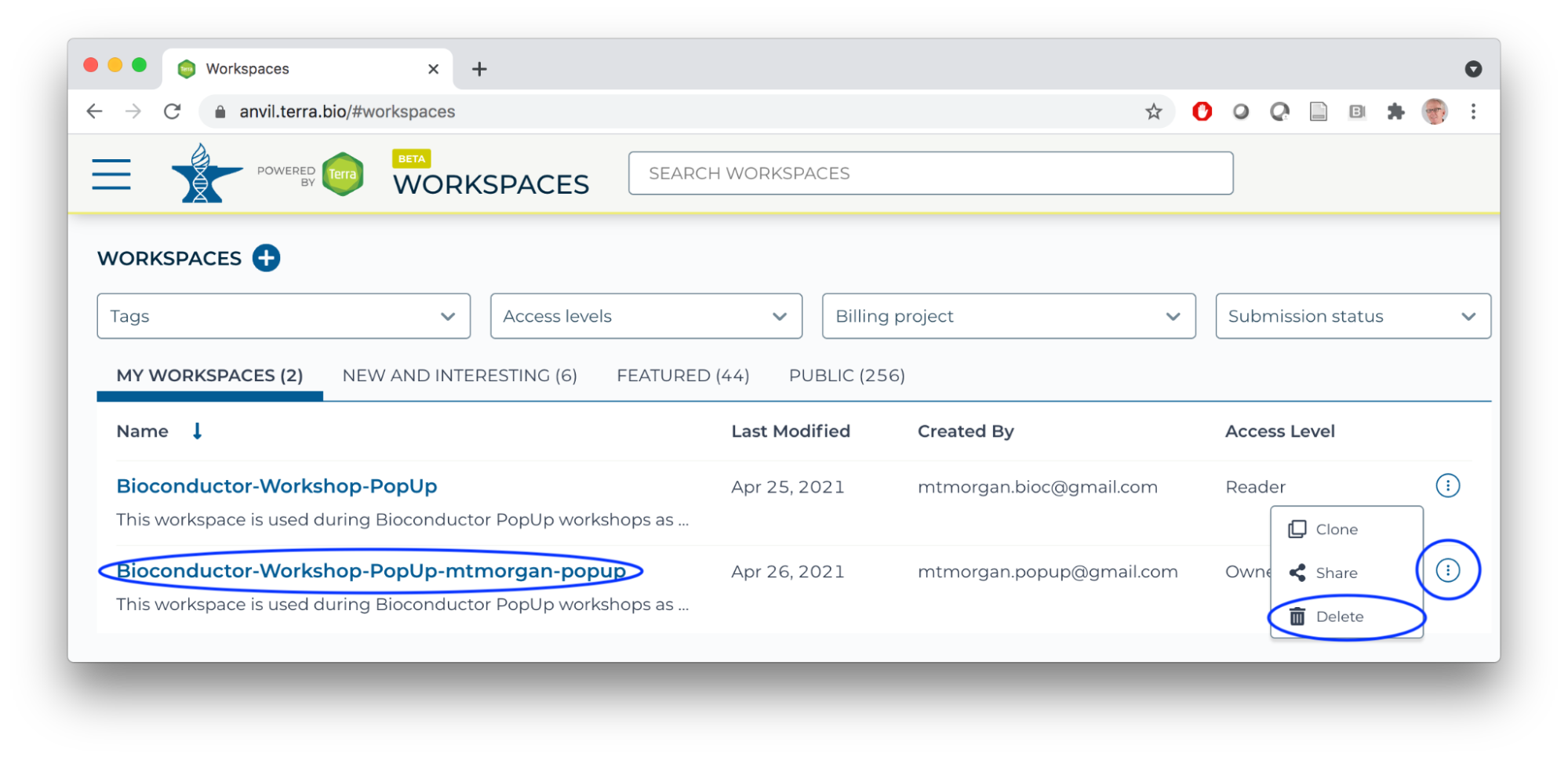
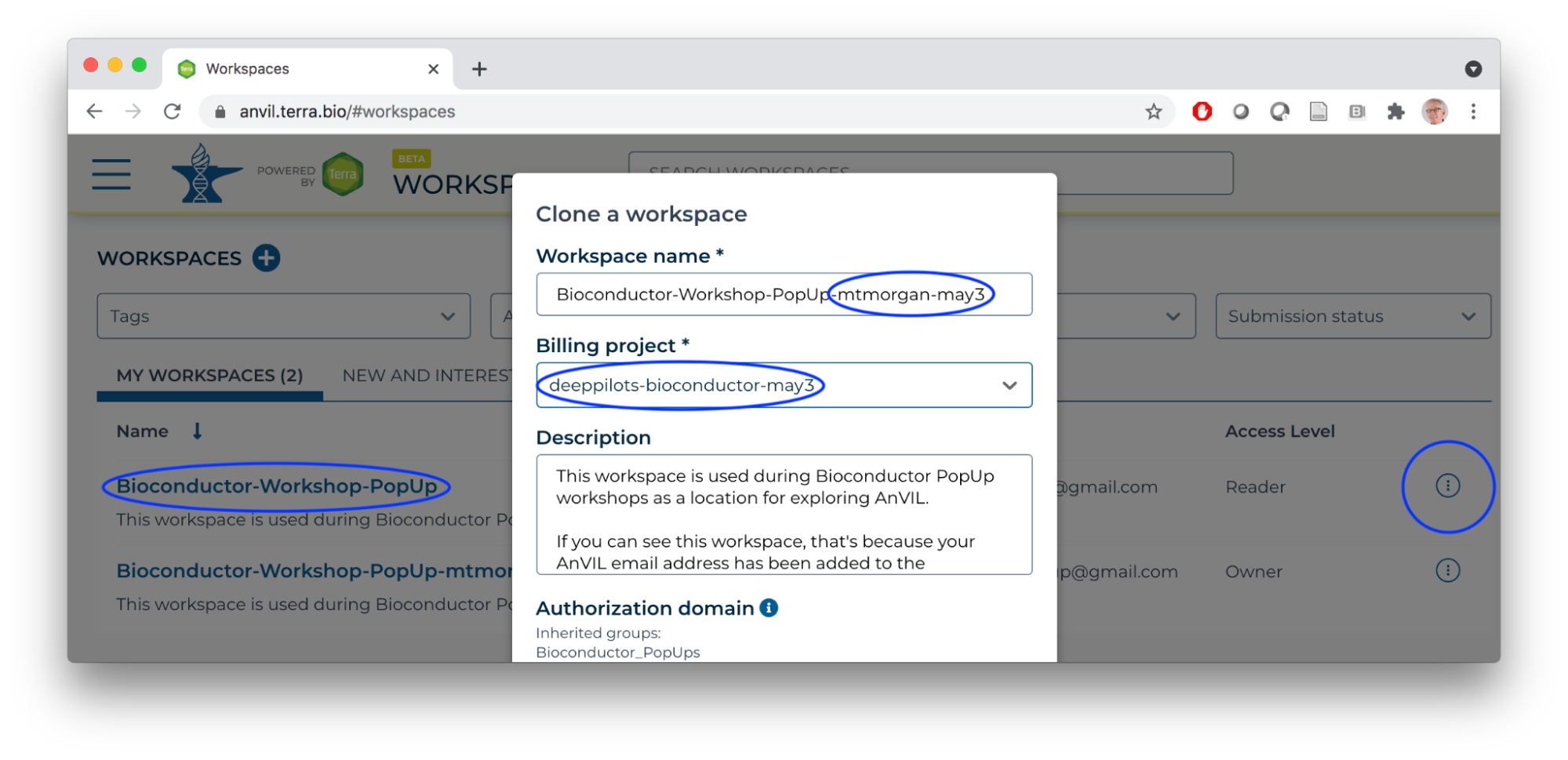
- Clone the Bioconductor-Workshop-Popup.
- Start an RStudio cloud environment.
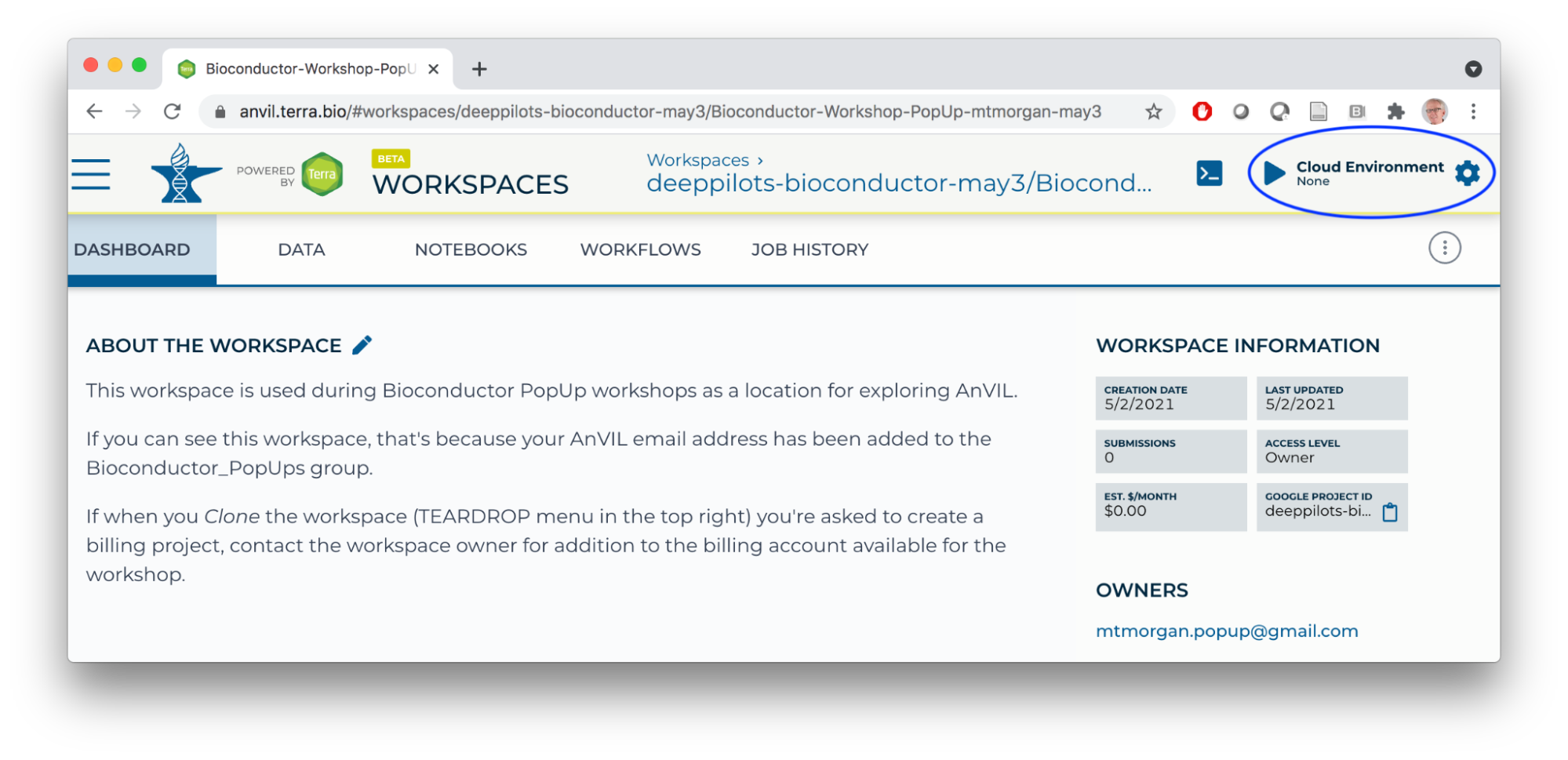
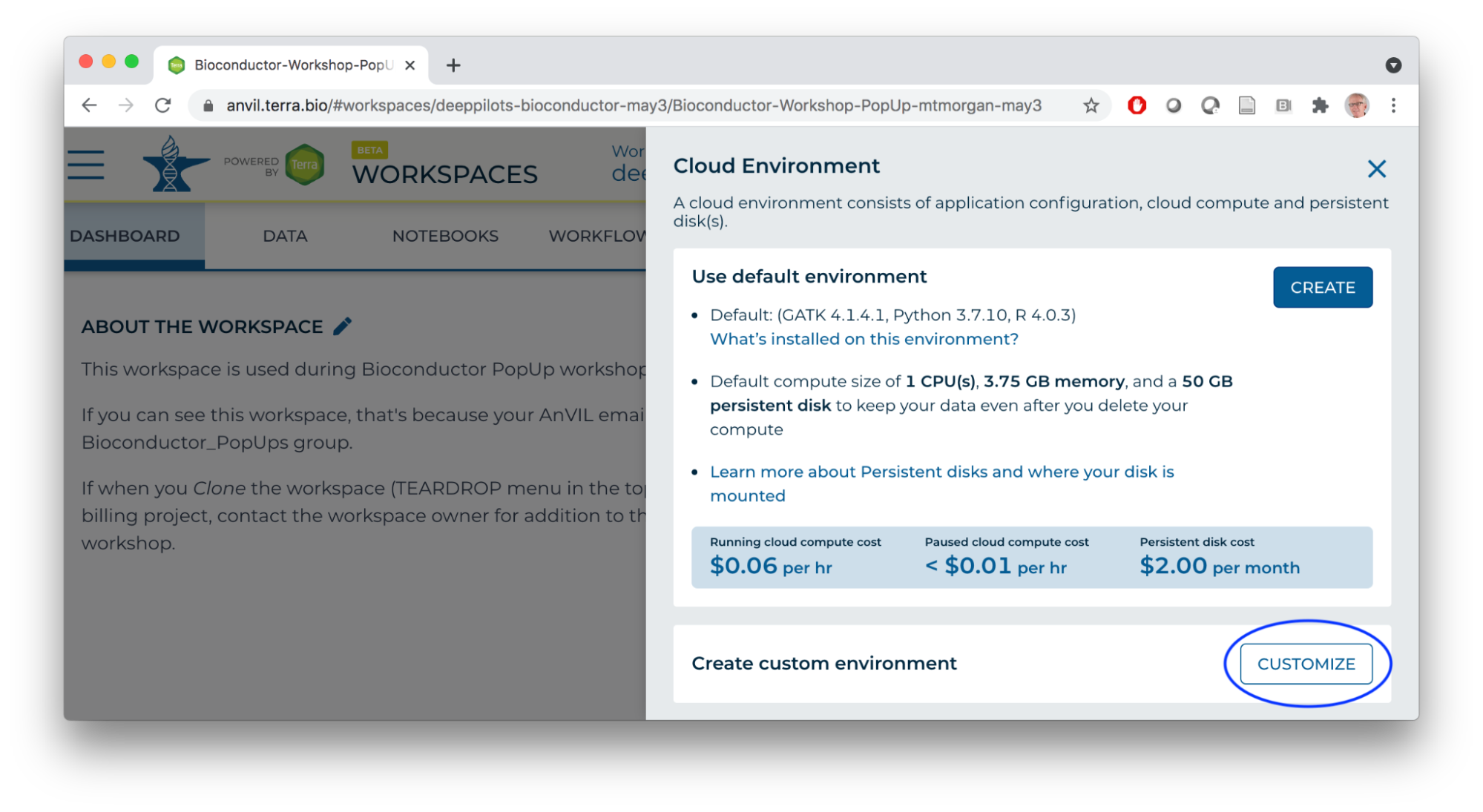
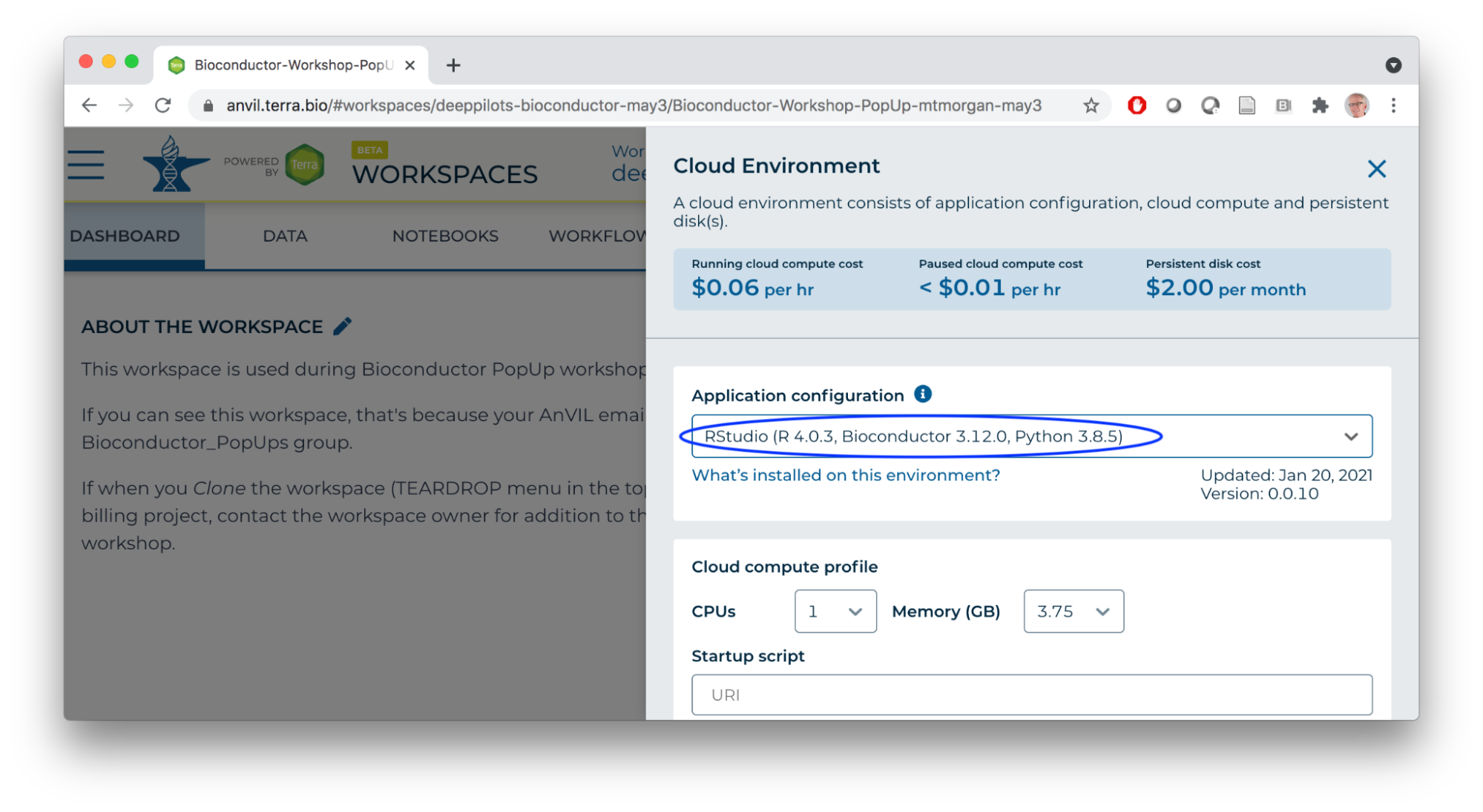
- Launch the cloud environment.
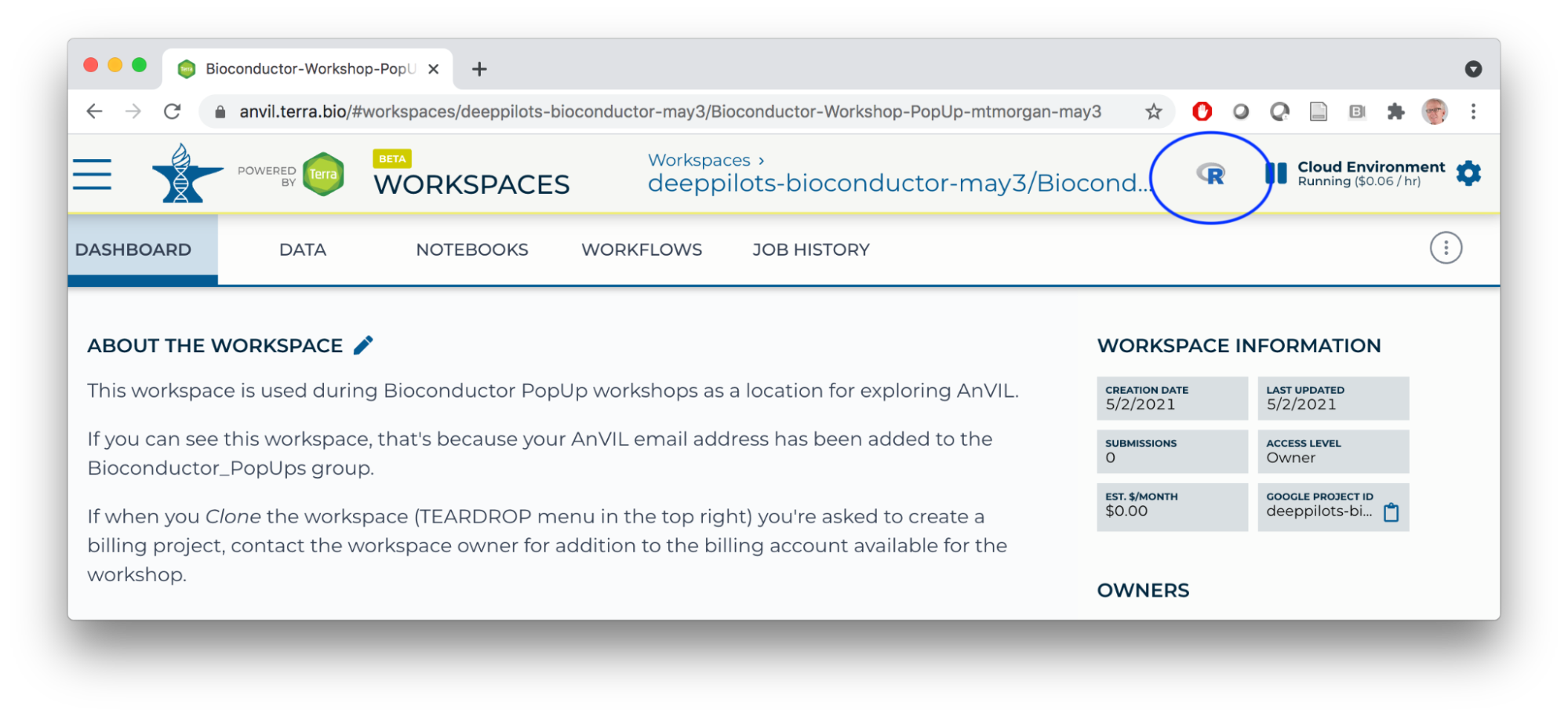
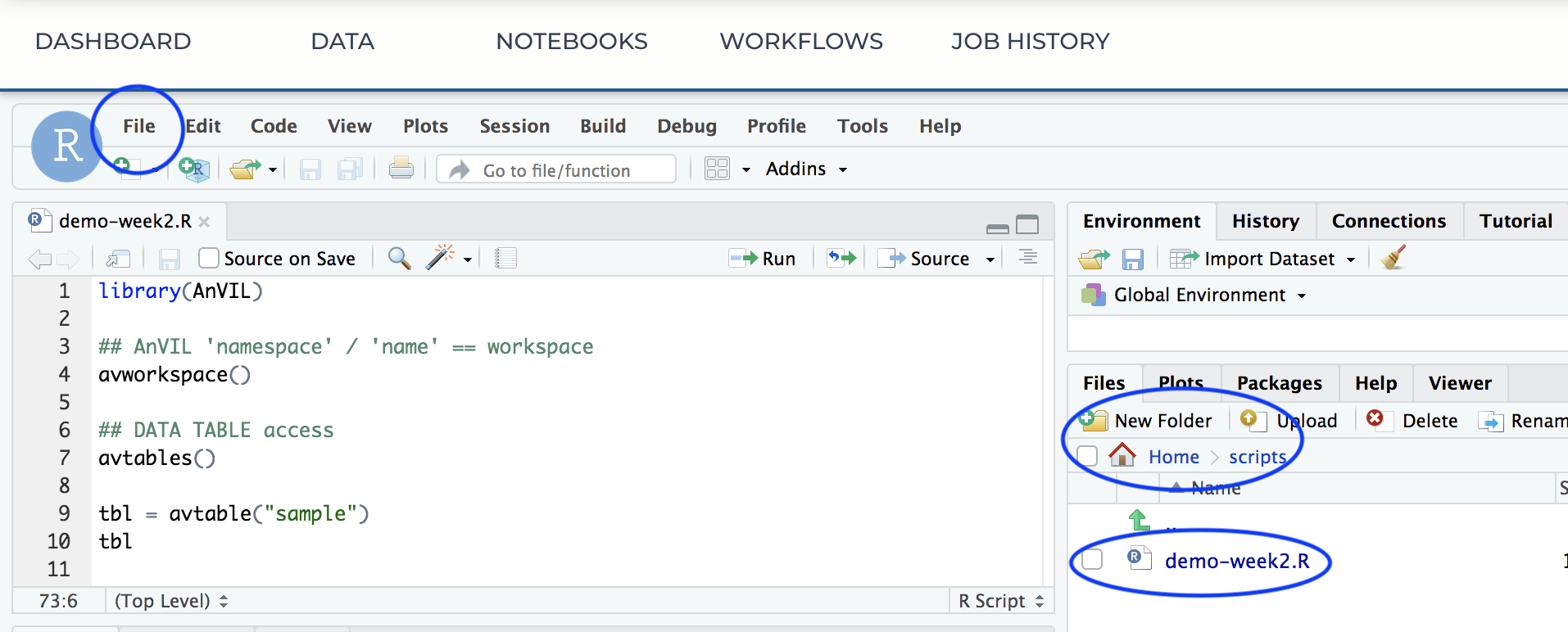
- Copy the week-2-demo.R script into a file on your cloud environment.
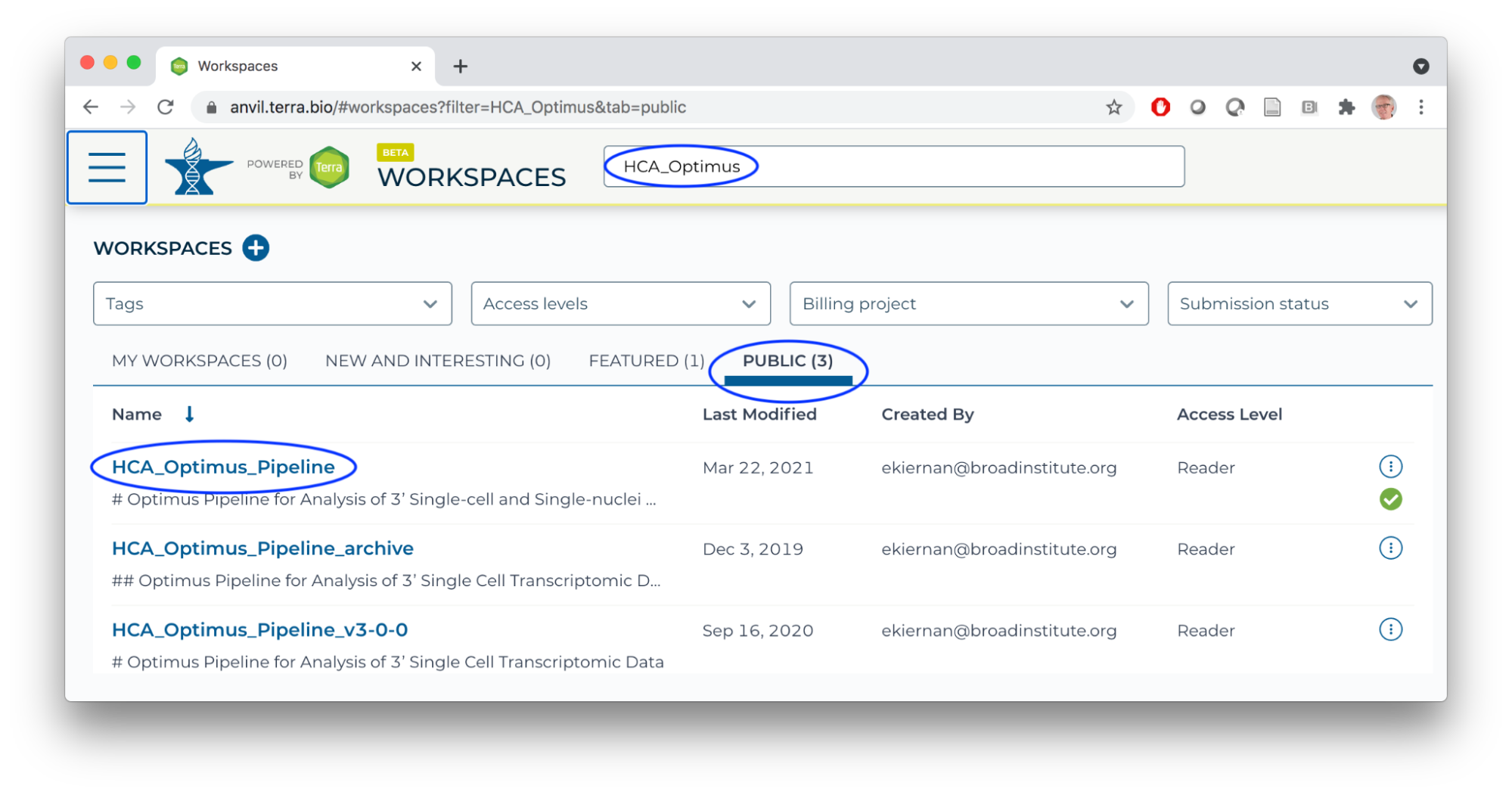
Workflows
- In a new browser tab/window, navigate (via the HAMBURGER) to the HCA Optimus Pipeline workspace. This workspace demonstrates how scRNA-seq fastq files can be transformed to a 'count matrix' for interactive analysis.
- Overall orientation: DATA TABLES serve as input to WORKFLOWS (scalable 'big data' computation).
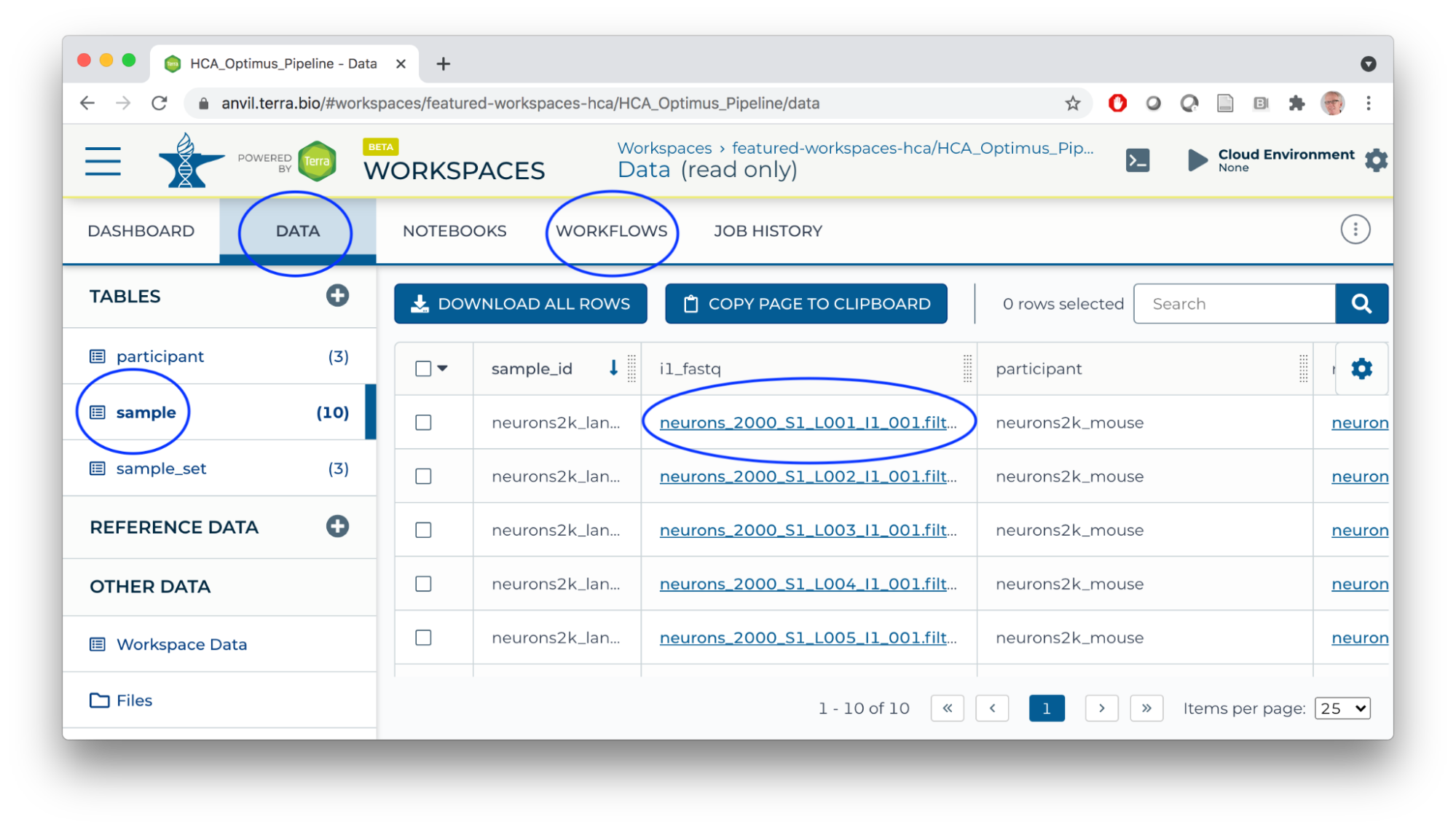
- Workflows transform big data using 'Workflow Description Language' scripts producing outputs (logs, results).
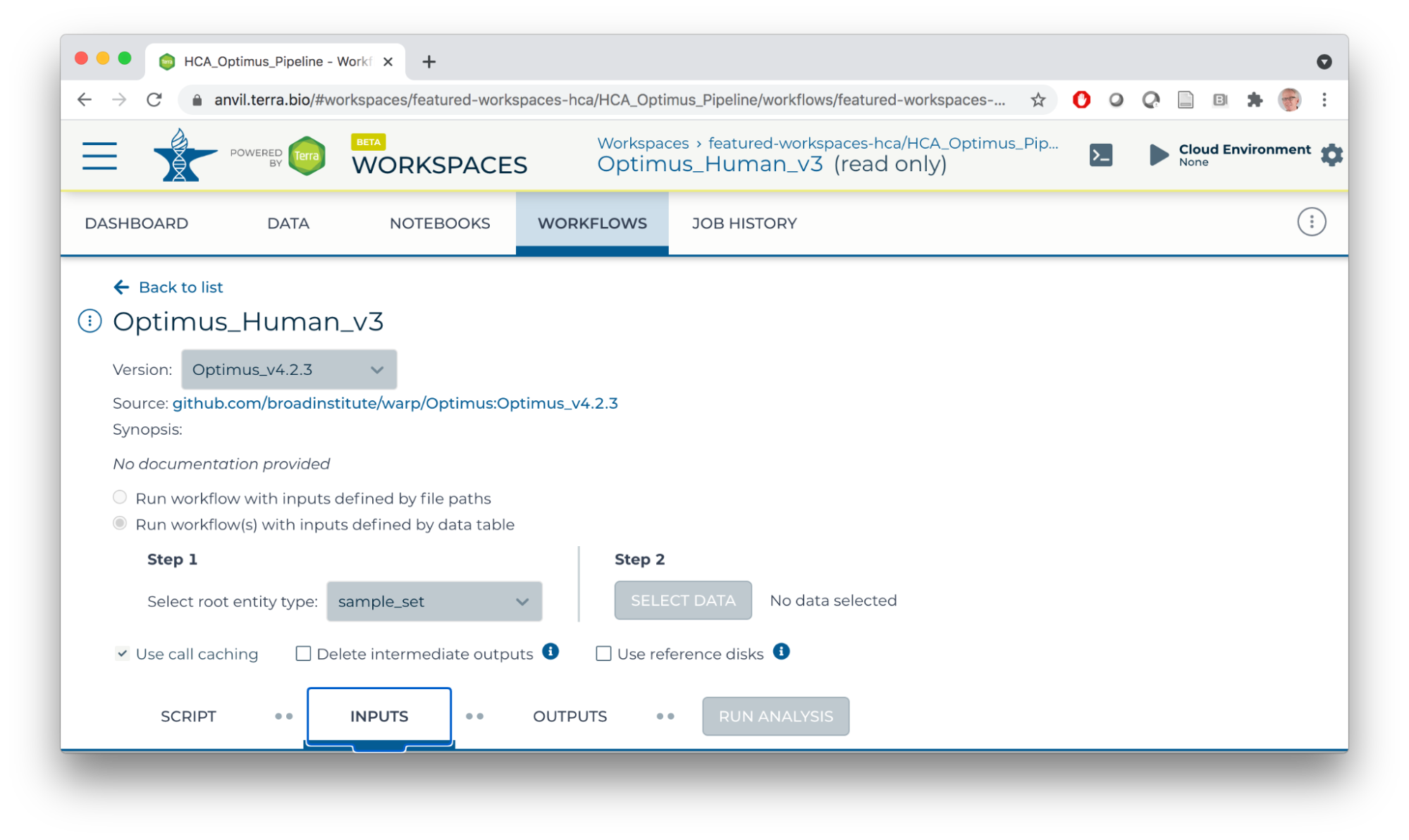 For this workflow:
For this workflow:
- Single-cell RNA seq analysis.
- Inputs are fastq files from individual samples.
- Scripts perform alignment, UMI processing, creating a 'count' matrix of gene x cell (sample) expression matrices, etc.
- Primary output of interest is a 'loom' file summarizing the count matrix.
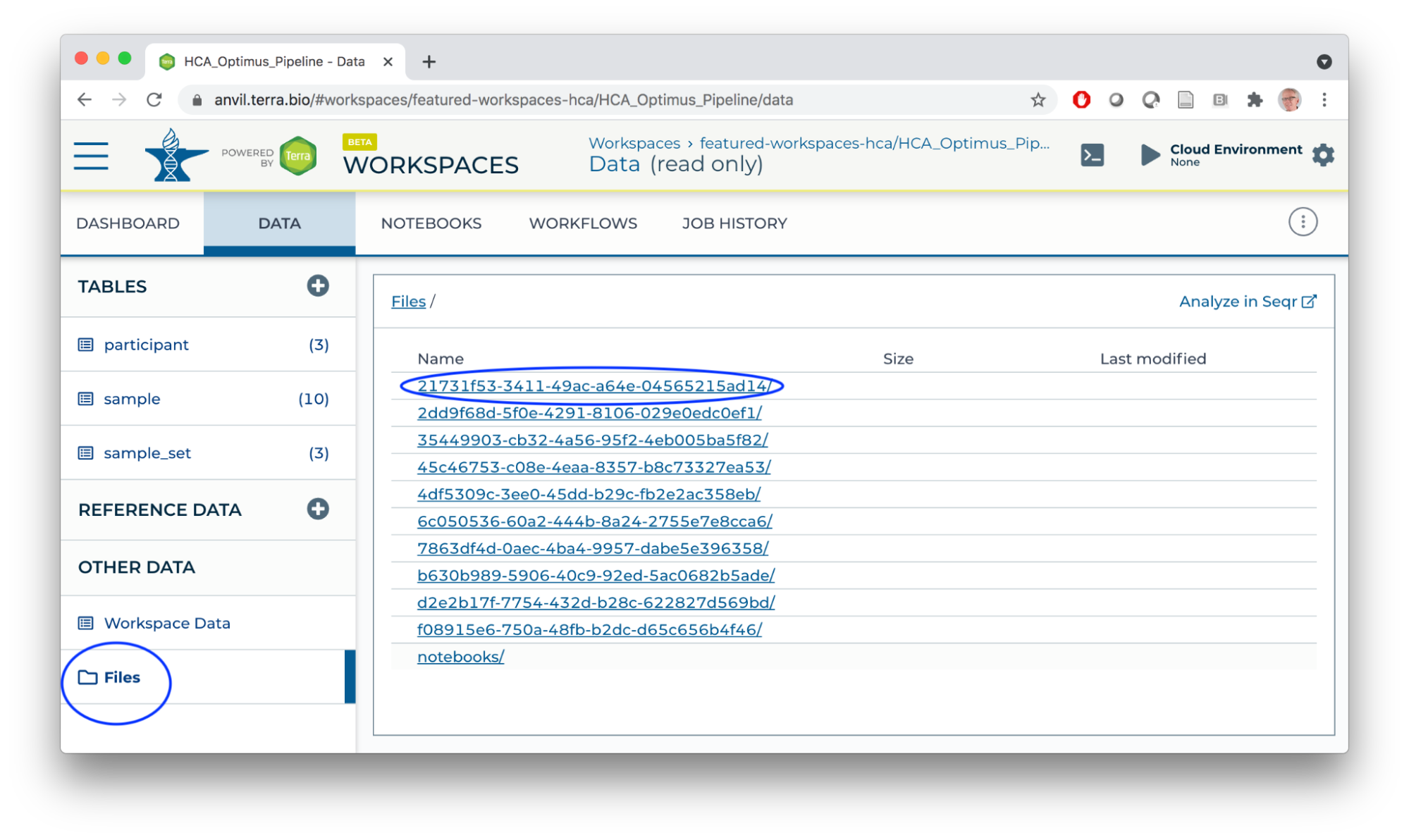
- Workspace bucket / Files store workflow outputs (each workflow run has a unique identifier; logs and results are located under the identifier). Buckets also provide a location for storing and sharing interactive analysis results.
The AnVIL Package
AnVIL Workspaces
hca = "featured-workspaces-hca/HCA_Optimus_Pipeline"
thousand_genomes = "anvil-datastorage/1000G-high-coverage-2019"
library(AnVIL)
avworkspace() # current workspace
avworkspace(hca) # set to HCA workspace
DATA TABLE Access
avtables()
tbl = avtable("sample")
tbl
tbl %>% count(participant)
## tbl %>% avtable_import()
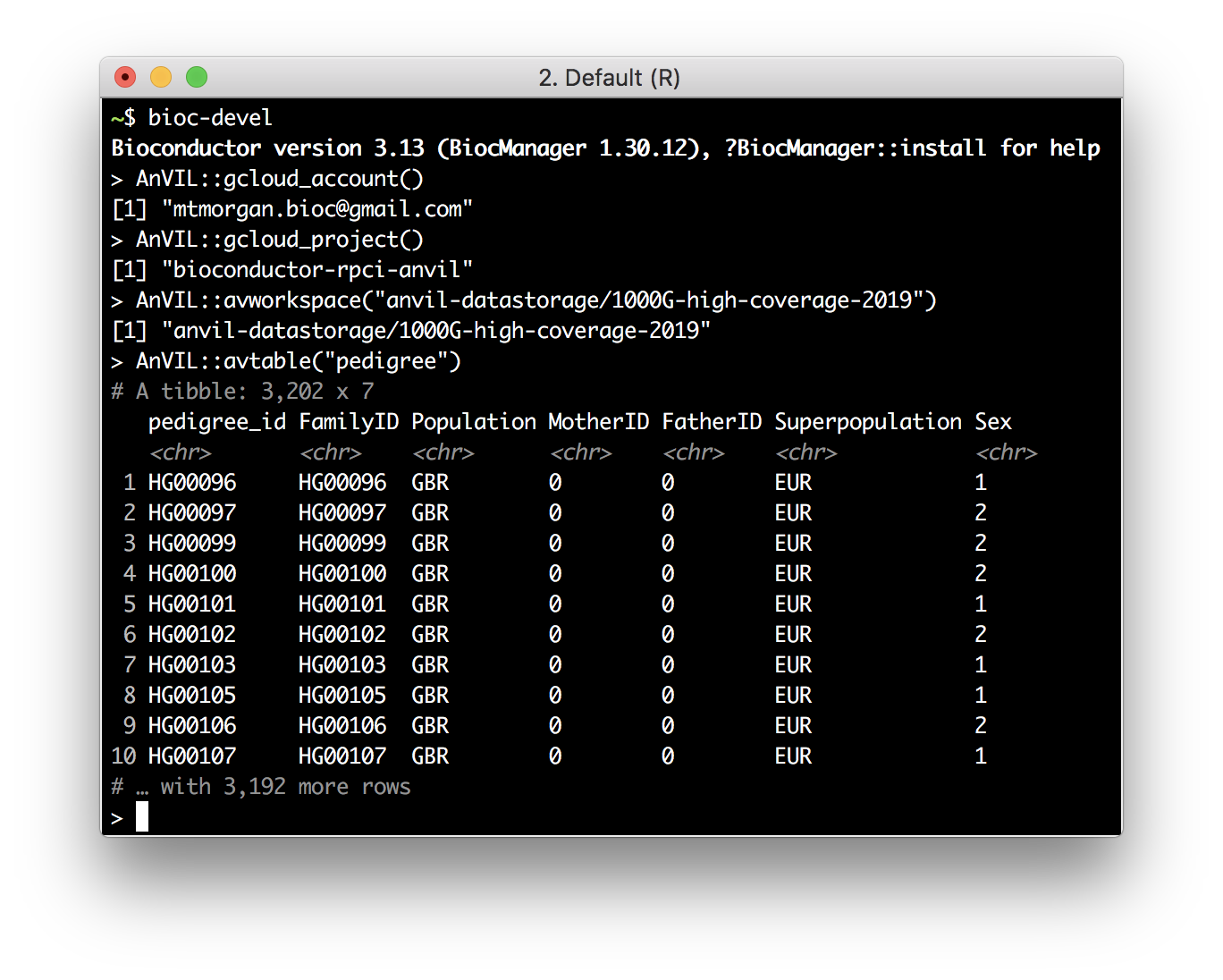
avworkspace(thousand_genomes)
avtables()
participant = avtable("participant")
participant
participant %>% count(POPULATION, sort = TRUE)
avtable("pedigree") %>%
count(Population, Sex) %>%
tidyr::pivot_wider(names_from = "Sex", values_from = "n")
## switch back to this workspace
avworkspace(hca)
Google buckets
## Copy files from google buckets to persistent disk
tbl = avtable("sample_set")
tbl
dir.create("~/loom")
gsutil_cp(tbl$loom_output_file, "~/loom/") # see also gsutil_rsync()
dir("~/loom")
## Workspace Bucket -- 'backup' or share persistent disk to workspace bucket
avbucket() # bucket associated with this workspace
gsutil_ls(avbucket())
avfiles_backup("~/scripts", recursive = TRUE) # see also avfiles_restore()
gsutil_ls(avbucket(), recursive = TRUE)
Fast Binary Package Installation
## do NOT update out-of-date packages yet
BiocManager::install("Bioconductor/AnVIL")
## RESTART R
AnVIL::repositories() # binary Bioconductor and CRAN package installation
## install and use LoomExperiment
AnVIL::install("LoomExperiment") # about 40 seconds, rather than 10's of minutes
sce = LoomExperiment::import("~/loom/pbmc_human_v3.loom")
Access AnVIL from Outside AnVIL
- Requires gcloud SDK installed on your computer.
- Use SDK to register your Gmail account and google billing project.
Access the AnVIL 'API'
leo = Leonardo()
leo
leo$listDisks()
terra = Terra()
tags(terra, "Workspaces")
wkspc =
terra$listWorkspaces() %>%
flatten() %>%
select(-starts_with("workspace.attributes"))
wkspc
Summary
What You've Accomplished
Setup
- Clone a workspace, launch an RStudio cloud environment
- Navigate between workspaces
Workflows
- Elements of workflow structure -- DATA TABLE inputs, scripts, File outputs
AnVIL Package
- Selecting workspaces
- Managing DATA TABLEs
- Moving data to and from google buckets
- Fast binary package installation (in the 'devel' version of the package)
- Advanced features, e.g., local use, API access
Next Steps
- Follow instructions at Set up billing with $300 Google credits to explore Terra to enable billing for your own projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Uploading workflows -- through GitHub / Dockstore, but also the Broad Methods Repository (YouTube); see also the WDL Puzzles workspace.
- Default name and namespace -- the runtime starts in a particular workspace, and the runtime knows the default namespace and name. So by default, I had
> avworkspace() [1] "deeppilots-bioconductor-may3/Bioconductor-Workshop-PopUp-mtmorgan" gsutil_cp(): CommandException: Downloading this composite object requires integrity checking with CRC32c, but your crcmod installation isn’t using...This is a bug that should be fixed in the underlying image for the runtime.